Picture this: you’ve just found a treasure chest, but instead of a traditional lock and key mechanism, it opens with a unique combination of numbers and letters only you know. In the world of cryptocurrency, this metaphorical chest is your digital wallet, and the combination? It’s represented by your private and public keys. These keys are like the digital signatures of the crypto universe, providing security and authentication to a world that thrives in a decentralized environment.
Introduction to Cryptography in Cryptocurrency
Cryptography: it’s not just the stuff of spy novels. It’s an essential component of cryptocurrency, making digital currencies secure, trustworthy, and reliable for daily transactions.
The Basics of Cryptocurrency Transactions
In the realm of digital currencies, every transaction made is a declaration that needs validation. Instead of having tangible coins change hands, cryptocurrency transactions are essentially a shift in values recorded on a blockchain. This decentralized ledger ensures transparency, but this also means the transactions should be secure to prevent fraudulent activities.
Role of Cryptography in Securing Transactions
Cryptography provides that much-needed shield against cyber-attacks and fraud. When transactions are made, they are encrypted using cryptographic algorithms, ensuring that only those with the correct set of keys can access and verify them. This not only ensures privacy but also boosts confidence in digital transactions.
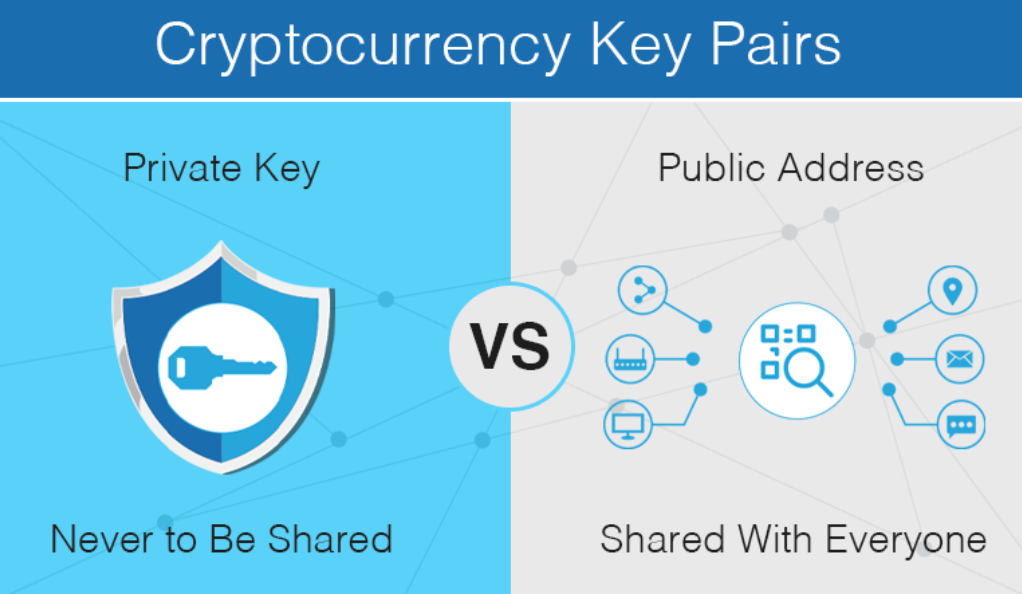
Understanding Public Keys
Think of a public key as your email address – a point of contact that you freely share. But instead of emails, it’s for crypto transactions.
Function and Purpose
The public key’s main function is to receive cryptocurrency. When someone wants to send you digital coins, they send it to your public key. This ensures that only your corresponding private key can access these funds, ensuring a layer of security and privacy.
How Public Keys Are Generated
A public key is derived from its corresponding private key through cryptographic algorithms. It’s a one-way journey: while a public key is generated from a private key, the reverse – deriving a private key from a public key – is mathematically infeasible. This ensures the security of the owner’s funds.
Diving into Private Keys
Imagine your deepest, darkest secret. Your private key is similar to that, a confidential piece of information that should never be shared.
The Crucial Role in Transaction Authorization
Private keys are instrumental in the world of cryptocurrency. When making a transaction, your private key is used to sign it, effectively proving it’s really you making the transfer. Without the correct private key, transactions from a digital wallet cannot occur, acting as a safety measure against unauthorized transfers.
Importance of Keeping Private Keys Secure

A lost or stolen private key is equivalent to losing your entire wealth stored in cryptocurrency. Since blockchain transactions are irreversible, once an ill-intentioned individual gets hold of your private key, they can deplete your funds. Hence, keeping it secure is paramount.
Relationship between Private and Public Keys
This duo is the heart and soul of cryptocurrency security, working seamlessly to keep your funds safe.
The Mathematical Link
The entwining of public and private keys is a wonder of modern cryptography. They’re mathematically linked in a way that the public key can receive funds and the private key can spend them, but without the private key ever being exposed or deduced from the public one.
How Transactions are Verified
The cryptographic handshake between these keys ensures secure transactions. When a transaction is made, the network cross-references it with the sender’s public key. If they match, it confirms the transaction’s legitimacy, but all without the private key ever being in the spotlight.
Risks of Mismanaging Keys
In the vast ocean of digital currencies, there are choppy waters and unforeseen storms one should be wary of.
Loss of Access
Misplacing a private key is a tragedy in the world of crypto. Without it, your cryptocurrency is lost in the abyss of the blockchain, never to be accessed again. It’s similar to losing a password to a vault full of gold.
Unauthorized Access & Thefts
Cyber thefts and hacks are rampant, and a compromised private key is a gateway for hackers to empty a victim’s digital wallet. It’s essential to understand that in the decentralized world of crypto, there’s no customer service or bank to call to freeze your funds. Once gone, it’s gone.
Best Practices for Key Management
Being informed and vigilant is your best defense against the pitfalls of the digital currency realm.
Using Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices that securely store a user’s private key. Think of them as ultra-secure USB drives for your cryptocurrency. They’re disconnected from the internet, providing an added layer against online hacking attempts.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Awareness is key. Be cautious of phishing scams, avoid sharing your private key, and always double-check website URLs before entering any sensitive information. It’s always better to be safe than sorry, especially in a realm as intricate as cryptocurrency.
Conclusion
The intricate dance between public and private keys is what makes cryptocurrency secure and trustworthy. As the digital world evolves and more people adopt cryptocurrencies, understanding and managing these keys becomes ever more crucial. After all, they’re not just strings of numbers and letters; they’re the gatekeepers of your digital treasure.
FAQs
Designed to be a unique and irretrievable identifier, a private key, once lost, cannot be regenerated. This feature maintains security but also emphasizes the key’s safekeeping.
No. A public key only allows someone to send funds to you. To withdraw or spend, the private key is essential.
Multiple options exist, from hardware wallets to paper wallets or encrypted digital storage. Choose based on your comfort and understanding.
Without the correct private key to sign the transaction, the network will reject and not verify the transfer.
While exchanges implement security measures, they remain hot targets for hackers. It’s always advised to keep long-term holdings off exchanges and in private wallets.